|
||||||
|
CHAENOMELES. Japanese quince. [Rosaceae] |
|
Japanese quince (C. japonica) is grown in gardens in Britain. Thirteen British miners are recorded on Chaenomeles. A key to the European miners recorded on Chaenomeles is provided in Bladmineerders van Europa. |
|
Key for the identification of the known mines of British |
1a > Leaf-miner and case-bearer: The larva lives outside the mine, protected by a case, and feeds on the underlying plant tissues via a hole cut in the epidermis. From that point it eats away as much leaf tissue as it can reach without fully entering the mine. Mine does not contain frass (Coleophora species) |
1b > Leaf-miner, but not a case-bearer: The larva lives mainly inside the mine. Mine usually contains frass. In later instars the larva may live sandwiched between two more or less circular sections cut from the leaf. |
| 3 |
2a > Leaf-miner and case-bearer: The species spends two years as a larva, the first one-and-a-half years in a small pistol-case, and in the second spring building a long straight case which is dark brown and rather distinctive. The lava lives from autumn until summer next year. In autumn a composite leaf case is made, shaped like the handle of a walking stick. Early in the following spring a tubular leaf case is made that in the end is rather large (10 mm) and is positioned vertically on the leaf; mouth angle 90°. |
|
Coleophora hemerobiella (Scopoli, 1763) [Lepidoptera: Coleophoridae]. |
2b > Leaf-miner and case-bearer: The larva feeds by inserting its head into small mines it creates on the leaves of birch, elm, alder, or hazel. Occasionally it is found feeding on other trees, or on herbaceous plants onto which it has accidentally Fallén. It forms two cases during its larval life. The first case is initially curved, smooth, laterally compressed with a bivalved anal opening, and about 2 mm long in September. During October it feeds, and adds a few rough collars of larval material around the oral opening. After hibernation, it feeds again in April and early May, adding more protruding collars until they equal or exceed the original smooth part of the case. At the same time, it expands the case girth by the creation of a silk gusset ventrally. The second case, 6 or 7 mm long, is formed in May, leaving the vacated first case attached to its last feeding mine. The new case is tubular with a trivalved crimp at the anal opening. The dorsum is formed from the edge of the leaf from which the case was cut. This results in a more or less serrated dorsal keel, depending on the plant species and the individual piece of leaf used. Considerable variation in the degree of serration can be found, even among specimens off the same tree. The case colour varies with food plant, from yellowish brown on birch, darkening through elm and hazel to dark brown on alder. The strongly curved young case is is a composite leaf case, the adult case is a tubular leaf case. The adult case is bivalved, about 7 mm in length; the mouth angle is around 30°. The case is straw coloured and almost always has a toothed dorsal keel (remnant of the margin of the leaf from which the case was cut). Neither larvae or cases of C. coracipennella, prunifoliae, serratella and spinella can be separated; from serratella. |
|
Coleophora serratella (Linnaeus 1761) [Lepidoptera: Coleophoridae]. |
3a > Leaf-miner: The larvae initially mining the leaves in a short, contorted gallery. As the larva develops it leaves the mine to feed externally, creating windows on the upperside of the leaves. Ovipossition at the leaf upperside, egg shell iridescent. Small, hook-like corridor, mostly in a vein axil. Frass in a very thick central line. The larva soon leaves the mine through an untidy hole and subsequenty feeds living freely on the leaf. Pupation occurs in a ribbed white cocoon spun on debris. The winter is passed in this stage.. |
|
Bucculatrix bechsteinella (Bechstein & Scharfenberg, 1805) [Lepidoptera: Bucculatricidae]. |
3b > Leaf-miner: A circular or oval brownish blotch with a central spiral of dense blackish frass (British leafminers), sometimes several mines in one leaf. Oviposition is at the leaf underside, well away from the leaf margin; the egg has a fine reticulate surface. The mine is a rather large, perfectly circular blotch without a trace of a preceding corridor. Around the dark centre the frass, glued to the upper epidermis is arranged in distinct arcs. Pupation in a silken cocoon, usually on detritus. |
|
Leucoptera malifoliella (O. Costa, 1836) [Lepidoptera: Lyonetiidae]. |
3c > Leaf-miner: A long, whitish smoothly-curved upper-surface mine with broken black frass. Oviposition is by means of an ovipositor; what remains is a small scar: no egg shell is visible at the start of the mine. From here a long, sometimes very long, slender, full depth corridor winds throught the leaf, not steered by leaf margin or the leaf venation. The midrib is crossed effortless; the corridor frequently also crosses itself; the section of the leaf cut off then usally turns brown and dies off. Frass in a narrow central line. The larva vacates the mine prior to pupation through an exit in the upper epidermis. The vacated larval chamber is proportionally much longer than in the case of Stigmella mines ( > 3 x longer than broad). Pupation in a silken cocoon suspended from threads attached to food plant or other vegetation. |
|
Lyonetia clerkella (Linnaeus, 1758) [Lepidoptera: Lyonetiidae]. |
3d > Leaf-miner: The larva mines the leaves of various roseaceous trees, such as blackthorn and apple, forming a gallery leading to a blotch. Eggs are deposited in the underside of a leaf, well away from the margin, often several per leaf. Around the oviposition site a cavity develops that in the end often leaves a hole in the leaf. Then a narrow, hardly widening, winding corridor, largely filled with a broad reddish brown frass line. The corridor abruptly widens into a wide, full depth blotch, that often lies against the leaf margin. The larva may leave its mine and continue elsewere, even on a different leaf. Note that the first blotch may already lie on a different leaf. Frass dispersed, in oval granules. Most frass is ejected through semicircular cuts along the outer limit of the blotch; part of it is often trapped in strands of silk under the leaf. The pupal cocoon is suspended from silken 'guy ropes' and closely resembles that of L. clerkella. |
|
Lyonetia prunifoliella (Hübner, 1796) [Lepidoptera: Lyonetidae]. |
3e > Leaf-miner: The mine is in the upper epidermis of a leaf, usually over midrib or vein. The mine is at first silvery, later with brown speckling. Silvery, upper-surface, epidermal tentiform mine, centered over the midrib or a heavy lateral vein. Unlike P. leucographella, with which this species shares some host plants, the upper epidermis looks dirty by the presence of numerous fine black-brown specks of frass. The epidermis remains without folds until the mine becomes strongly contrated. Young mines look like a streak of silver on top of a vein. |
|
Phyllonorycter corylifoliella (Hübner, 1796) [Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae]. |
3f > Leaf-miner: Elongated, lower surface, tentiform mine with one strong fold in the lower epidermis. Pupa in a white cocoon, in which no frass in incorporated; all frass in a clump in the mine. Before ecdysis the pupa works itself out of the mine through the floor in the mine. |
|
Phyllonorycter cydoniella (Denis & Schiffermüller, 1775) [Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae]. |
3g > Leaf-miner: The mine is upper side and silvery, over the midrib. Leaf later may fold upwards, concealing the mine. Oviposition is on the base of the midrib. From there an epidermal corridor is made, running towards the leaf tip. The corridor then is widened into an epidermal, silvery blotch, finally into a longitudinally contracted tentiform mine. Frass in fine, shining grains, mostly in a line over the midrib, rarely in a mass in a corner of the mine. The epidermis of the mine has a number of yellow spots, but never the black specks that are apparent in P. corylifoliella. |
|
Phyllonorycter leucographella (Zeller, 1850) [Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae]. |
3h > Leaf-miner: A large mine with a strong crease in lower epidermis. Leaf-edge often folded downwards. Lower-surface, yellow-green tentiform mine with a few sharp folds in the epidermis. In Rowan the mine is parallel to the leaf margin, in Cherry usually between two lateral veins. The light brown cocoon lies in a wide cocoon, in which no frass is incorporated; all frass is accumulated in a clump in an angle of the mine. Before hatching the pupa penetrates the mine wall; generally the exuvium remains stuck halfway out of the mine. |
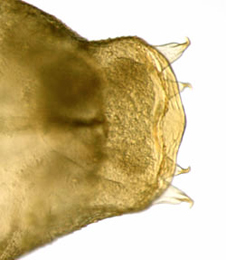 Phyllonorycter sorbi pupa, cremaster, dorsal Image: © Willem Ellis (Bladmineerders van Europa) |
|
Phyllonorycter sorbi (Frey, 1885) [Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae]. |
3i > Leaf-miner: The young larva mines the leaves of its foodplant then hibernates. It will then mines leaves or flowerbuds, then blossom or leaves. Branched, sometimes stellate, brownish, very transparent, sometimes long corridor that contains no frass. All frass is ejected through a number of tiny openings that generally are close to a vein. Only the young larvae are miners. |
|
Recurvaria nanella (Denis & Schiffermüller, 1775) [Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae]. |
3i > Leaf-miner: Usually a very small, pear-shaped, upper-surface blotch, most of it stuffed with reddish brown frass. Often several mines in a leaf. Ovipisition is already in May, but the larvae hatch late and initially develop very slowly; only against the end of summer the mines become apparent. The larvae remain in the mine and hibernate in the fallen leaves. The bright-coloured frass and their large number makes these mines very conspicuous in autumn, despite their small size. The weevils feed pinhole-sized windows in the leaf upperside (maturation feeding). |
|
 Rhamphus oxyacanthae larva, dorsal Image: © Willem Ellis (Bladmineerders van Europa) |
|
Rhamphus oxyacanthae (Marsham, 1802) [Coleoptera: Curculionidae]. |
| 3j > Leaf-miner: The reddish frass is linear, later in arcs, finally dispersed. Long corridor, that widens only little, and winds freely through the leaf, not influenced by the venation. In thick, sun-exposed leaves the mine may be much shorter, especially in Cotoneaster, Malus and Pyrus. Frass brown, in arcs.. |
|
? Stigmella oxyacanthella (Stainton, 1854) [Lepidoptera: Nepticulidae]. |
| Last updated 02-Jul-2019 Brian Pitkin | ||

